Description
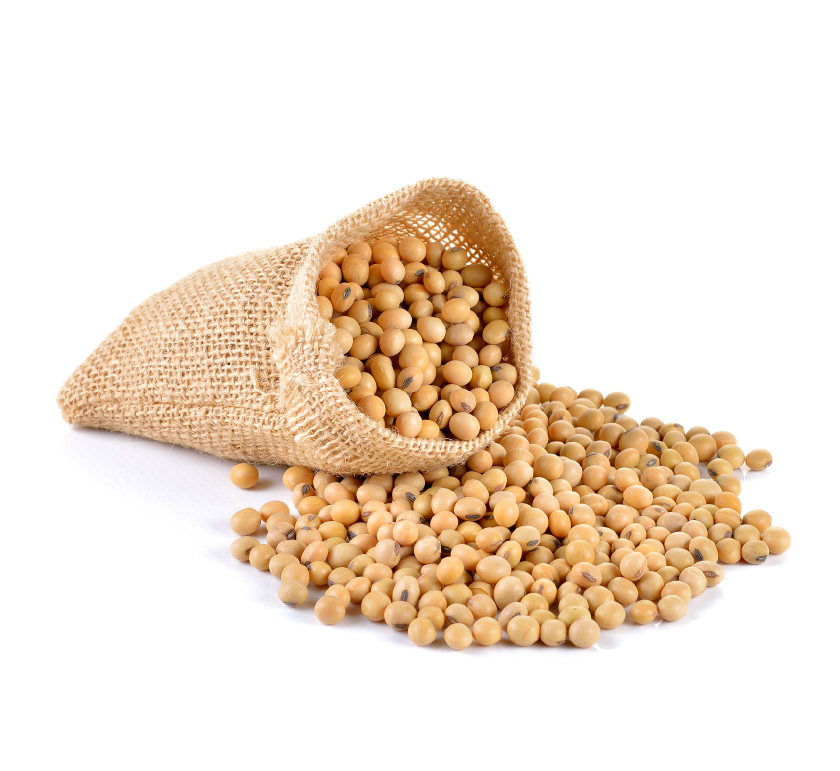
Soybean for human and animal feed
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (Glycine max)[3] is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes.[4]
Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption).[5]
• Quality: Standard Export Quality
• Type: Non-GMO, Fit For Human Consumption
• Moisture: 13.5% Maximum
• Max Splits: 20%
• Protein: 35% Basis, 34% Minimum
• Max Color: 2%
• Oil Content: 18.5% Basis, 18.0% Minimum
• Test Weight: 54 Pounds/Min/Bushel
• Total Damaged Kernels: 3% Max
• Foreign Matter: 2% Max
• Radiation: Normal
• Heat Damaged Kernels: 0.50% Maximum.
• Crop: Current